상속
- 기본 클래스의 속성과 기능을 파생 클래스에 물려주는 것
- 가장근접한 클래스를 가져오는것
- 기본클래스: 상속해주는 클래스, 부모 클래스
- 파생 클래스: 상속받는 클래스, 자식 클래스
1) 상속 정의시
class 클래스이름 : public(접근지정자(기본 private)) 물려받은 클래스이름
- 접근지정자는 public으로 가져올 시 public으로 지정된 것들만 가져올 수 있다 그것 보다 좁은 private는
가져올 수 없다. 하지만 private로 접근지정자를 설정하면 기본 클래스를 모두 private로 가져올 수 있다.
2) 상속의 목적
1. 간결한 클래스 작성
2. 클래스간의 계층적 분류 및 관리의 용이함
3. 클래스 재사용과 확장을 통한 소프트웨어 생산성 향상
업캐스팅
파생클래스 포인터가 기본클래스 포인터에 치환되는 것
파생클래스의 객체를 기본클래스의 객체처럼 사용 가능
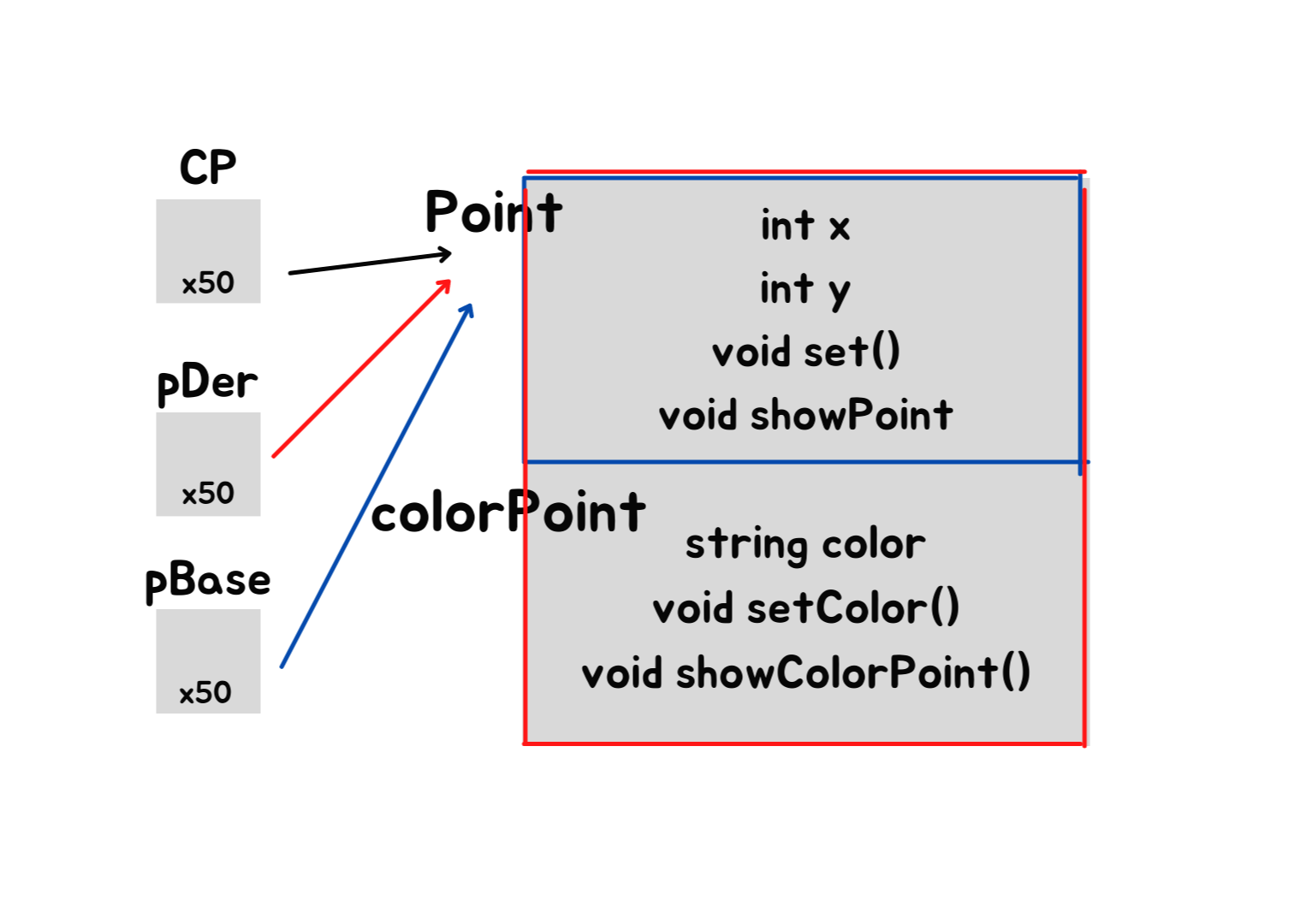
ex1)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Point {
int x, y;
public:
void set(int x, int y) { this->x = x; this->y = y; }
void showPoint() {
cout << "{" << x << "," << y << "}" << endl;
}
};
class ColorPoint : public Point {
string color;
public:
void setColor(string color) { this->color = color; }
void showColorPoint();
};
void ColorPoint::showColorPoint() {
cout << color << ":";
showPoint();
}
int main() {
ColorPoint cp;
ColorPoint* pDer = &cp;
Point* pBase = pDer;
pDer->set(3, 4);
pBase->showPoint();
pDer->setColor("Red");
pDer->showColorPoint();
}
다운 캐스팅
- 기본클래스의 포인터가 파생클래스의 포인터에 치환 되는 것
- 업캐스팅에서 다이 원래의 형으로 돌려주는 것
Protected
클래스 외부에서는 protected 멤버에 접근할 수 없지만 해당 클래스의 하위 클래스(파생된 클래스, 자식 클래스)에서는 접근 가능
ex1) 에러가 나는 부분은 주석처리후 왜 에러가 발생하는지? 이유를 찾으시오.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point {
protected:
int x, y;
public:
void set(int x, int y);
void showPoint();
};
void Point::set(int x, int y) {
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
void Point::showPoint() {
cout << "(" << x << "," << y << ")" << endl;
}
class ColorPoint :public Point {
string color;
public:
void setColor(string color);
void showcolorPoint();
bool equals(ColorPoint p);
};
void ColorPoint::setColor(string color) {
this->color = color;
}
void ColorPoint::showcolorPoint() {
cout << color << ",";
showPoint();
}
bool ColorPoint::equals(ColorPoint p) {
if (x == p.x && y == p.y && color == p.color)
return true;
else
return false;
}
int main() {
Point p;
p.set(2, 3);
/*p.x = 5; //main(외부)에서 호출, 상속관계도 x 에러가 발생
p.y = 5;*/ //main(외부)에서 호출, 상속관계도 x 에러가 발생
p.showPoint();
ColorPoint cp;
/*cp.x = 10; //main(외부)에서 호출하므로 에러가 발생
cp.y = 10;*/ //main(외부)에서(외부) 호출하므로 에러가 발생
cp.set(3, 4);
cp.setColor("Red");
ColorPoint cp2;
cp.set(3, 4);
cp.setColor("Red");
cout << ((cp.equals(cp2)) ? "true" : "false");
return 0;
}
상속에서 생성자
- 생성자를 호출하면 자기자신의 생성자 부터 제일 위의 부모의 생성자까지 호출이 된다.
- 하지만 실행은 제일 위의 부모 생성자 부터 호출을 처음했던 생성자순으로 내려가면서 실행된다.
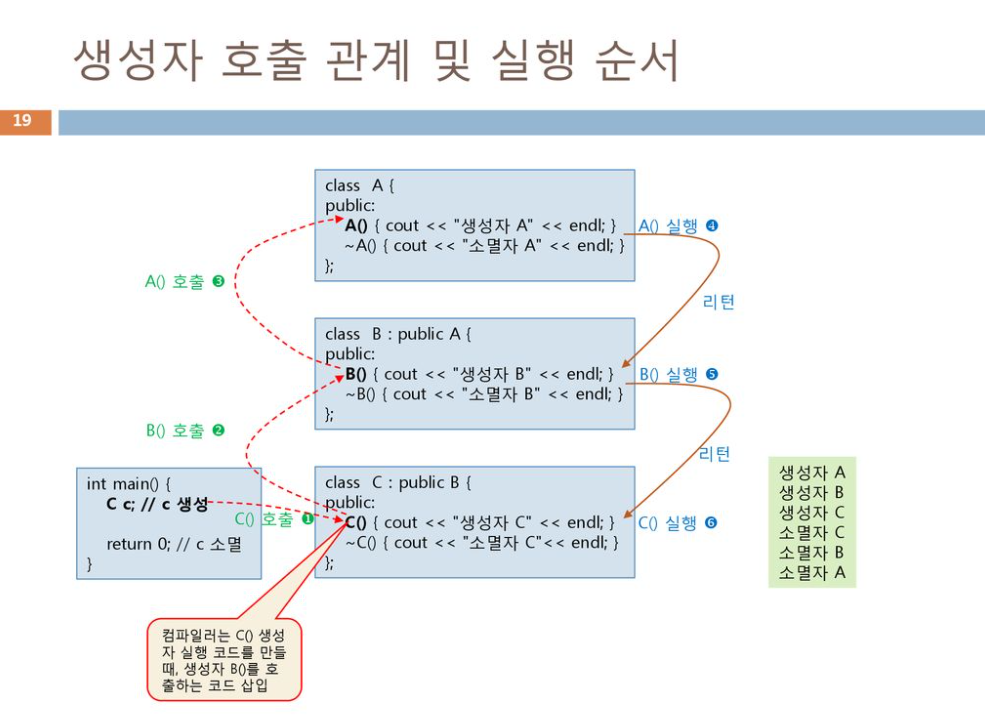
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class TV {
int size;
public:
TV() { size = 20; }
TV(int size) { this->size = size; }
int getSize() { return size; }
};
class WideTV : public TV {
bool videoIn;
public:
WideTV(int size, bool videoIn) : TV(size) { // 부모생성자중에 매개값 1개 받는것으로가라
this->videoIn = videoIn;
}
bool getVideoIn() { return videoIn; }
};
class SmartTV : public WideTV {
string ipAddr;
public:
SmartTV(string ipAddr, int size) : WideTV(size, true) {
this->ipAddr = ipAddr;
}
string getIpAddr() { return ipAddr; }
};
int main() {
SmartTV htv("199.0.0.1", 32);
cout << "size=" << htv.getSize() << endl;
cout << "videoIn= " << boolalpha << htv.getVideoIn() << endl;
cout << "IP = " << htv.getIpAddr() << endl;
return 0;
}❓ 스마트티비에서 모두 다 값을 설정해주면 안되나요? -> 안됨
이유는 ? : videoIn은 private로 지정되어 클래스안에서만 접근가능하므로
❗종합예제
class Point{
int x, y;
public:
Point(int x, int y){ this->x = x; this->y = y;}
int getX(){ return x;}
int getY(){ return y;}
protected:
void move(int x, int y){ this->x = x; this->y = y;}
};
다음 main()함수가 실행되도록 Point 클래스를 상속받는 ColorPoint클래스를 작성하고
전체 프로그램을 완성하라.
int main(){
ColorPoint cp(5,5,"RED");
cp.setPoint(10,20);
cp.setColor("BLUE");
c.show();
}
결과출력
BLUE 색으로 (10,20)에 위치한 점입니다.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// 클래스 포인트
class Point{
int x, y;
public:
Point(int x, int y) { this->x = x; this->y = y; }
int getX() { return x; }
int getY() { return y; }
protected:
void move(int x, int y) { this->x = x; this->y = y; }
};
class ColorPoint :public Point {
string color;
public:
ColorPoint(int a, int b, string color) : Point(a, b) {
this->color = color;
}
void setColor(string color) {
this->color = color;
}
void setPoint(int x, int y) {
move(x, y);
}
void show() {
cout << color << "색으로 (" << getX() << "," << getY()
<< ")에 위치한 점입니다." << endl;
}
};
int main() {
ColorPoint cp(5, 5, "RED");
cp.setPoint(10, 20);
cp.setColor("BLUE");
cp.show();
}
상속 지정
- 상속 선언시 private,public,protected의 3가지 중 하나 지정
- 기본 클래스의 멤버의 접근 속성을 어떻게 계승할 지 지정
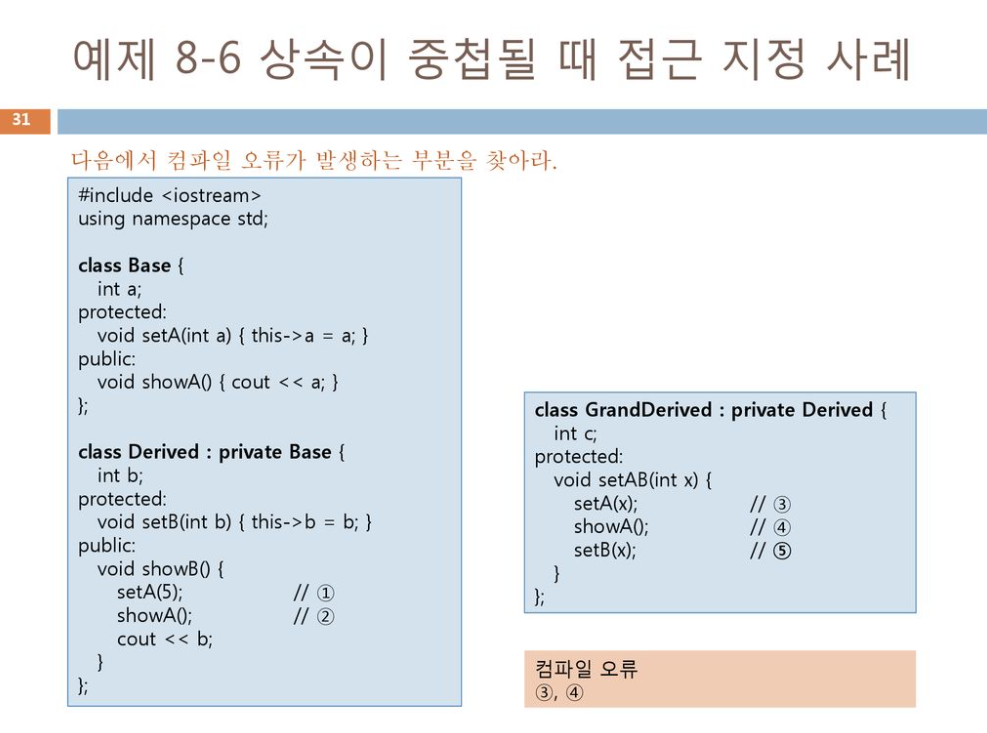
class Derived : private Based를 class GrandDerived : private Derived로 상속받으면 class Base의 모든 것들이 private로 바뀌어 class GrandDerived에서는 Class Base로 접근 불가능
'Programming > C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C++ 마지막 종합 실습! (0) | 2021.04.23 |
|---|---|
| C++ 입출력스트림 (0) | 2021.04.23 |
| C++ static (0) | 2021.04.21 |
| C++ 얕은복사 깊은복사 (0) | 2021.04.21 |
| C++ 참조자 (0) | 2021.04.20 |

댓글